Sunflowers
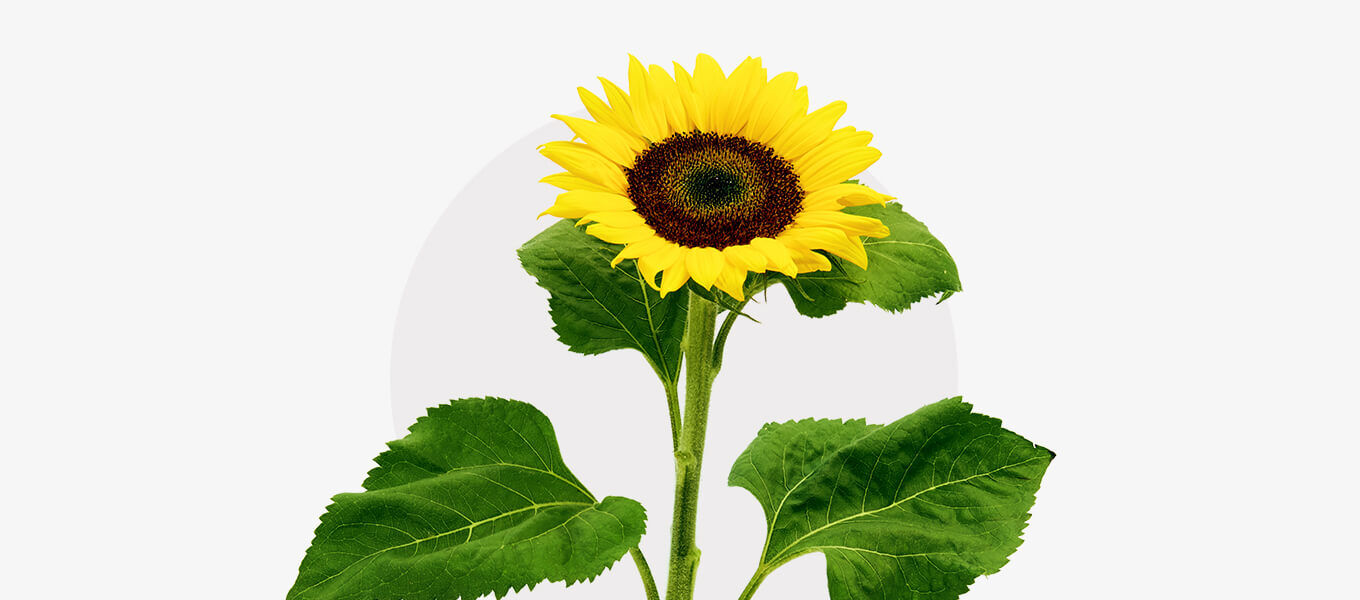

No other plants are as symbolic of summer as sunflowers. They bloom from July to October and transform countless fields and gardens into a sea of bright yellow flowers. In addition to their attractive visual effect, sunflowers are also particularly valuable for the food industry - their oily seeds can be used in a variety of ways and are easy to process. In the following article, you will learn all about the origin, appearance and proper care of sunflowers.

Sunflower meaning - Why are sunflowers given as gifts?
The botanical name of the sunflower is Helianthus annuus. The name comes from the Greek: "helios" means sun and "anthos" means flower. The sunflower therefore stands for sun, light and life. Whether as "I like you" or "the sun rises with you" - it is suitable as a gift for everyone. The flowers come into their own as a single stem, in a bouquet or as a potted plant.
Appearance
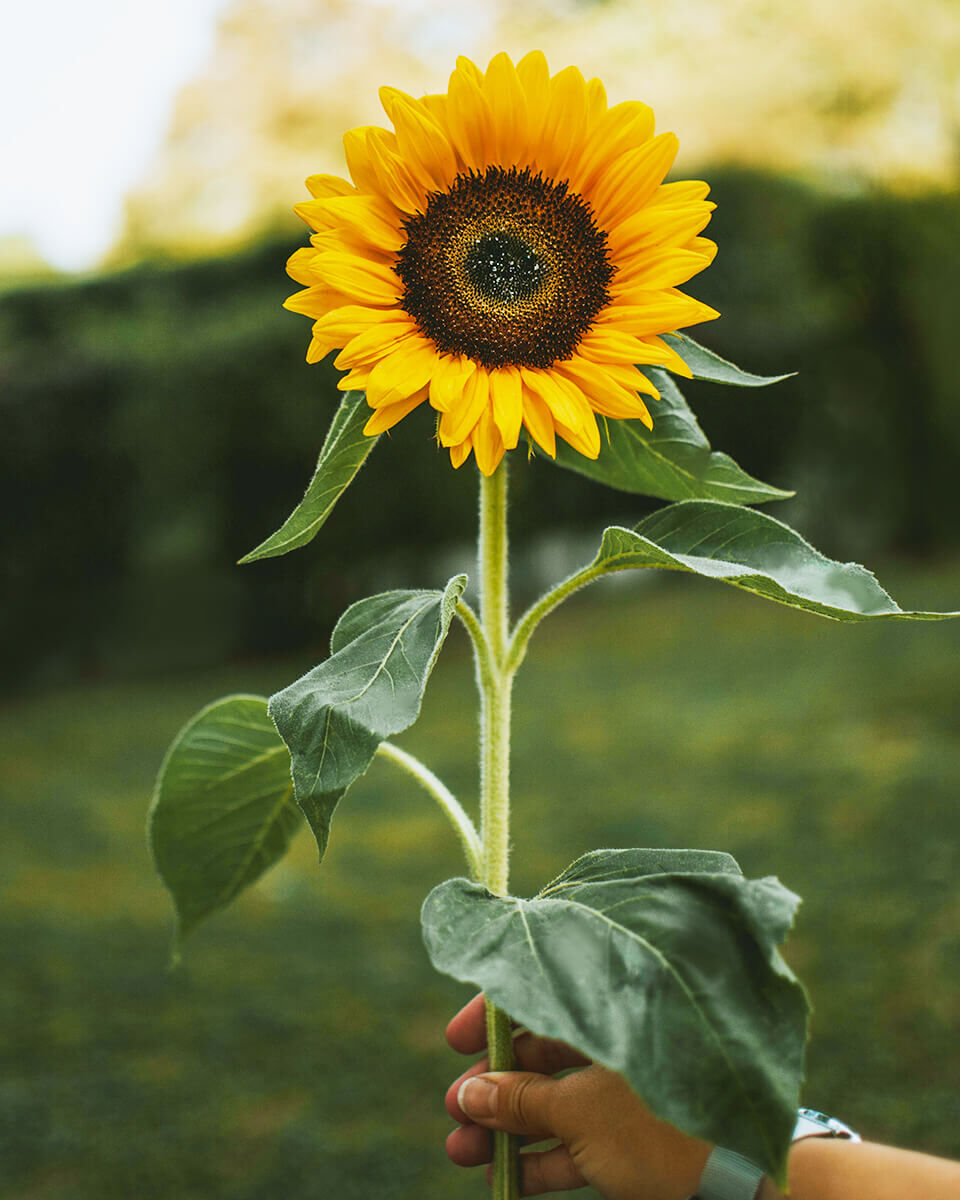

Sunflowers belong to the aster family. They stand out not only because of their distinctive flower heads with their radial yellow, orange or red-yellow flamed petals, but often also because of their impressive height.
Sunflower leaves
The annual sunflowers develop a strong, slightly hairy flower stalk with heart-shaped to lanceolate large leaves.
Flowers
The sunflower blooms from June until autumn with palm- to plate-sized flower heads. These have a corolla of yellow to orange-red ray florets. The centre of the flower consists of brown tubular flowers.
Location and soil
As the name suggests, the sunflower likes a sunny location in nutrient-rich soil. In order for the plant to grow quickly, it needs plenty of water. It develops a long taproot with a dense root felts to absorb water.
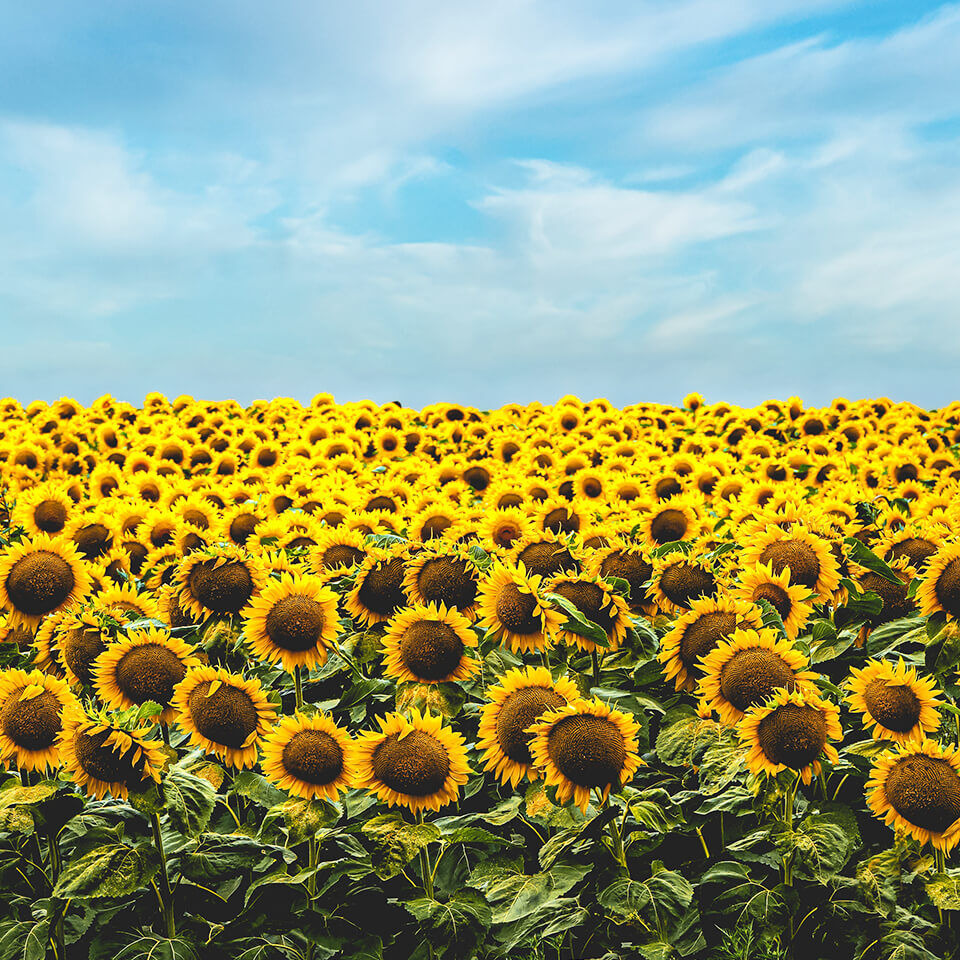

Why do sunflowers all look in one direction?
The young plants move with the sun from east to west every day during their growth phase until the leaves and flower buds are formed; experts call this process heliotropism. Special groups of cells below the flower buds are responsible for this, which ensure that the side facing away from the sunlight produces more of the growth hormone auxin and thus grows faster. This causes the stem to bend and the flower to lean towards the sun.
Why do sunflowers stop facing the sun later?
If the sunflower is in bloom or has already formed its fruit, it no longer changes its position as the stem becomes woody. The open flower then points permanently towards the east.
Origin
The wild sunflower originally comes from North and Central America. Archaeological finds prove that they were already being cultivated around 2500 BC on the Mississippi and in what is now Mexico. Spanish conquistadors became aware of these interesting plants in the middle of the 16th century and brought them to Europe, where sunflowers were initially only cultivated as ornamental plants. In the 19th century, Russia began extracting oil from sunflower seeds. Today, sunflowers are cultivated on a large scale for industrial purposes, with the USA, China, Russia, France and North America being the main areas of cultivation.
Sunflower varieties & important species

The sunflower belongs to the Asteraceae family. The sunflower genus is very extensive with more than 60 species. In addition to its function as an ornamental plant, it is also cultivated as a crop. Accordingly, there is a great deal of interest in breeding and therefore a wide range of varieties on the market.
A distinction is made in terms of flower characteristics, such as varieties with high nectar production. They are well suited as bee pasture. A distinction is made between early to very late flowering varieties, with low or high oil content or high grain yield. Depending on the species and variety, there are annual or perennial sunflowers. Perennial species and varieties grow in clumps. They spread via rhizome tubers. There are also pollen-free varieties that are well suited as cut flowers.
Depending on the variety, sunflowers bloom in traditional yellow, but also in orange, red, bronze or brown. There are also semi-double and double varieties. There is a large selection of Helianthus annus, the annual sunflower. It is sown as an annual crop and grows up to three metres high.
Large sunflowers
Extra large sunflowers can reach an impressive height of up to 2.5 metres. Their flower sizes then usually vary depending on the variety. While some varieties only produce a single large main flower, others have a branched growth habit. These secondary shoots then have several flower heads. So-called giant sunflowers even reach heights of up to 5 metres and then have flowers with a diameter of up to 60 centimetres. Titan' or 'KingKong' are among the larger varieties that grow up to 4 metres high. The largest sunflower entered in the Guinness Book of Records was an impressive 9.17 metres. The sunflower is seed-fertile, which means that the seeds of large plants give rise to large varieties.
Small sunflowers
Smaller sunflower varieties are ideal for use on balconies and patios. They do not exceed the dimensions of containers, boxes and pots and are equally decorative with their yellow and typical flowers. However, they are mostly cultivars. This means that they hardly ever produce seeds. If they do produce seeds, they will not necessarily produce smaller varieties the following year. This is associated with a smaller amount of pollen. This has the advantage of reducing pollution and contamination of outdoor oases with this pollen, which often triggers allergies. Well-known varieties include 'Yellow Peck', 'Teddy Bear' and 'Sunspot'.
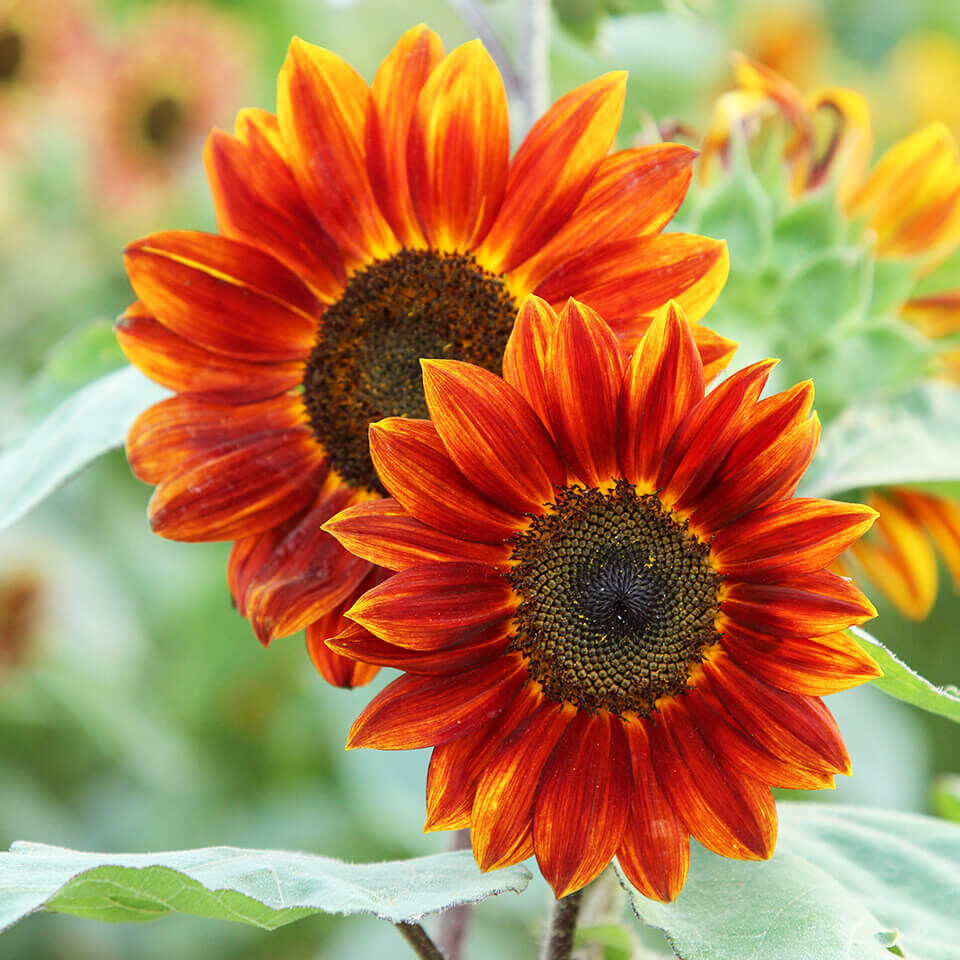

Red sunflower
Sunflowers are not necessarily yellow-flowered. Some varieties also have reddish, orange-coloured or even brownish ray florets. These in turn can vary in colour, sometimes with lighter edges or yellow on the inside.

Perennial sunflower
Perennial sunflowers are available as herbaceous sunflowers. Many of them are even hardy. Their flowers are smaller, the plants grow up to two metres high and their sunflower seeds are not edible.
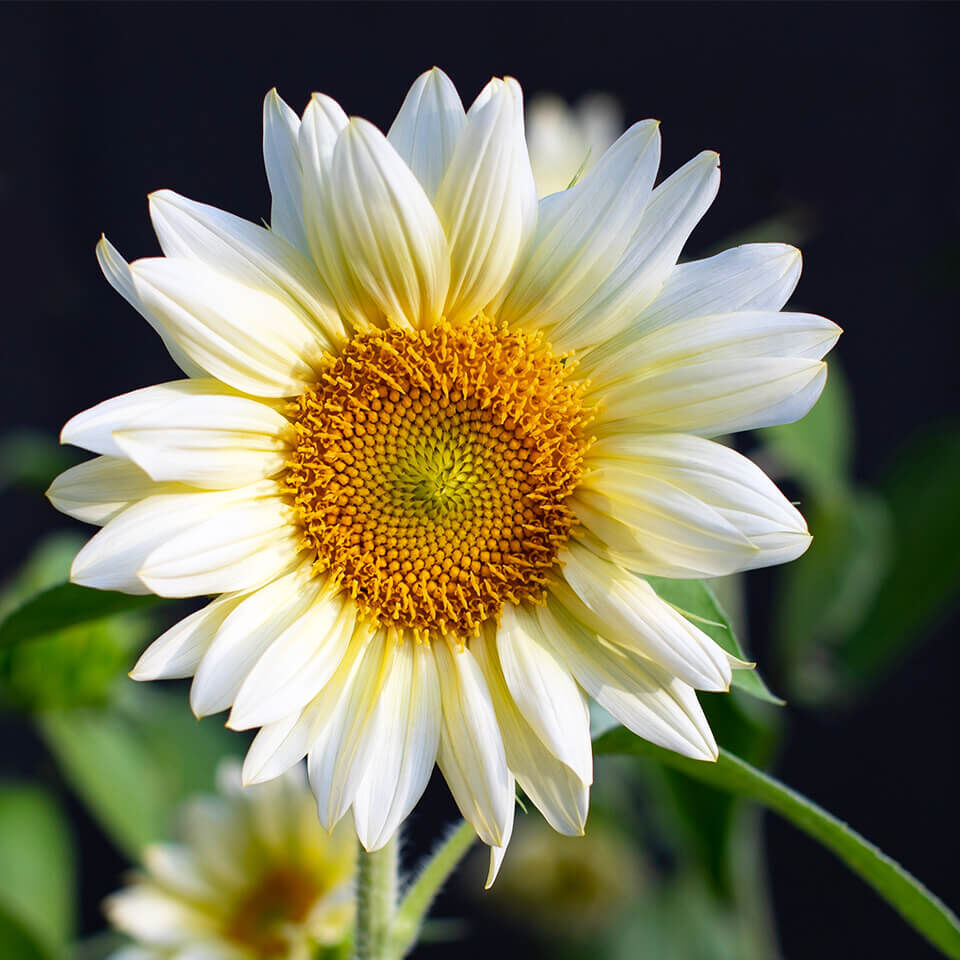

White sunflowers
There are also sunflower varieties that have white ray florets. A well-known variety is `Pro Cut White Nite` or `Italian White`. These are cultivars whose seeds do not necessarily produce a white variety the following year.
Giant sunflower
As already mentioned for the large sunflowers, there are also so-called giant sunflowers. In order for them to reach their gigantic height of over six metres, or 9.17 metres as in the case of the sunflower entered in the Guinness Book of Records, optimal site conditions must be provided in addition to the genetic conditions. Helianthus giganteus, as the species is called, requires a sunny location with nutrient-rich, well-drained soil and good moisture.
Dwarf sunflower
The so-called dwarf sunflower is suitable for cultivation in pots or containers and grows to a height of around one metre.
Mexican sunflower
The Mexican sunflower is not a sunflower in the true sense of the word. It is actually Tithonia rotundifolia. Due to the similar appearance of its flowers, it is mistakenly referred to as a sunflower, but the only thing it has in common with the latter is that it also belongs to the Asteraceae family, but not to the Helianthus genus.

Sunflower care & planting - the most frequently asked questions
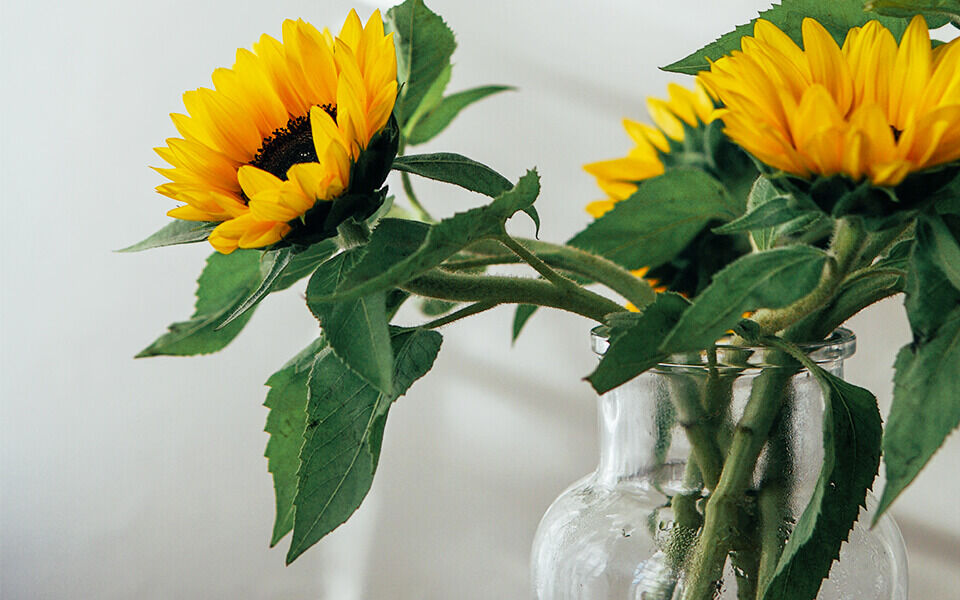

How do I care for sunflowers in a vase properly?
The general care tips apply to sunflowers in a vase. The only difference with the sunflower is that it likes lukewarm water - but not hot water!
Sunflowers can be grown from seed indoors in spring. The young plants are planted out from the end of May. Sunflowers also like to self-seed in the garden.
Depending on the weather and variety, the seeds should be planted in a sunny location in nitrogen-rich soil between the end of March and the beginning of May. A suitable cover will protect the young shoots from possible night frosts. To ensure that the sunflowers grow vigorously, you need to make sure they have a sufficient water supply. The visual effect is enhanced if several plants are sown in a loose group or strictly in rows 30 to 50 centimetres apart. Flowering, towering sunflowers can then serve as an attractive privacy screen in the summer months, for example along a property boundary.
If you don't sow your sunflowers directly in the bed from May, you can pre-grow sunflowers indoors from April using sunflower seeds in seed pots.
A sunny, sheltered location is ideal. Large solitary sunflowers are a decorative element in flower beds or on the patio. Sunflowers are a must in cottage gardens or cottage garden beds.
It takes around three to four months from sowing to flowering. The first seedlings appear after around 14 days. After three to four months, the sunflower is fully grown and should be given a sturdy stick to support it.
There are annual and perennial species and varieties ranging from small "dwarf sunflowers" to the approximately 4.80 metre "giant sunflowers".
Sunflowers in the garden grow very quickly and should be watered and fertilised regularly during this phase. If you sow directly, you must protect the seedlings from being eaten by snails.
Daily watering is strongly recommended for thirsty plants. Under no circumstances should they dry out - not even for a short time. The location should be bright, but again not full sun, as this makes it very easy for them to dry out quickly. Faded flowers should not be removed, as they continue to ripen and are still ornamental even as mature flowers without petals.
Sunflowers grow best in a sunny and warm location in moist and nutrient-rich soil. Sunflowers thrive best in areas with a consistently mild climate and plenty of sunshine.
Many sunflower varieties are cultivars which, when sown the following year, no longer produce what was hoped for. They mutate back to their original components. Some varieties are also perennial, provided they have an ideal location over the winter. However, it is generally advisable to sow new seeds every year or to plant young plants that have been germinated and pre-sprouted in the nursery. In this respect, sunflowers are considered annual plants.
What do you do with sunflowers when they have faded?
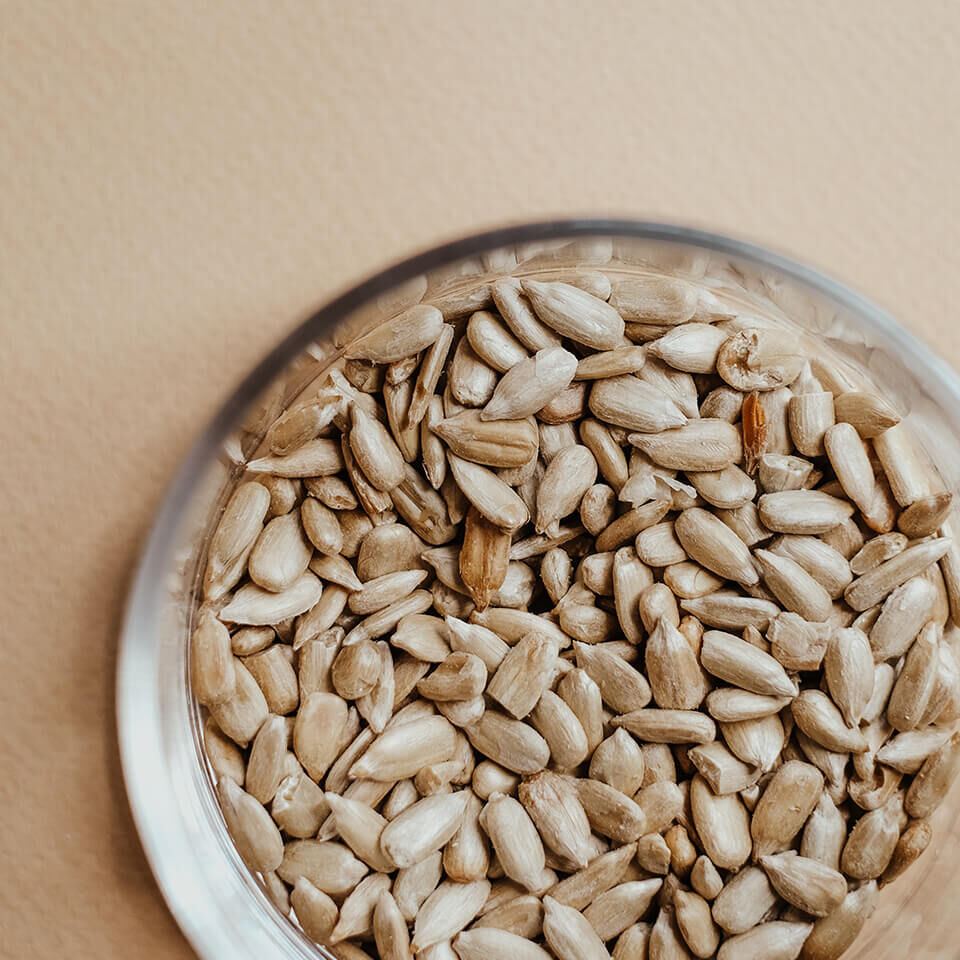

After flowering, the sunflower heads continue to develop and ripen. The head remains on the plant to ripen, or it can be left to ripen in a dry place. However, the flower head should be harvested before the flower is fully open. The sunflower seeds can be harvested from September, can be sown again the following year and are also a tasty treat for birds.
For a healthy diet, washed sunflower seeds - eaten in moderation - are highly recommended: in addition to vitamins A, B, D, E and K, they are rich in calcium, iron and selenium as well as phosphorus and, above all, magnesium. Due to their high folic acid content, the white-grey seeds are highly valued as a snack, especially by pregnant and breastfeeding women. Although the fat content of the seeds is high - 100 grams consist of about half fat - around 90 per cent of the stored fatty acids are unsaturated and therefore do not represent a major burden on the cholesterol balance.
The mild-tasting sunflower oil, which is obtained by pressing the seeds, is ideal for salad dressings, baking or steaming and is therefore very popular. In addition to its use as an edible oil, sunflower oil is also used in the pharmaceutical sector and for the production of paints and varnishes.
The seed heads are a decorative winter ornament. The seeds of annual sunflowers are valued by birds as fat and protein-rich food in the winter months. The flower stalks are cut back close to the ground in spring.
Young sunflower seedlings with up to four leaves can tolerate late frosts down to around minus 5 degrees Celsius. At lower temperatures down to minus 8 degrees Celsius, the leaves turn yellow, but the plants continue to grow without any problems when the temperatures rise again. Sunflowers with four to eight leaves or more react sensitively to late frosts.
During the growth phase, sunflowers need a lot of water and should be watered regularly - preferably early in the morning - depending on the weather. The indicator is "drooping" flower heads.
Possible diseases and pests
Sunflower rust can often be found on the large green leaves of the sunflower in summer. This is characterised by yellow-brown spots on the upper side of the leaves. The affected leaves should be disposed of promptly in the rubbish bin.
Aphids love sunflowers. Birds peck freshly planted seeds out of the ground, also eat young seedlings and peck at sunflowers as they mature. Young seedlings should also be protected from snails and slugs.